- ‘Divergence of character’ (character displacement or sympatric speciation) postulates: “during the incessant struggle of all species to increase in numbers, the more diversified these descendants become, the better will be their chance of succeeding in the battle of life. Thus the small differences distinguishing varieties of the same species, will steadily tend to increase till they come to equal the greater differences between species of the same genus, or even of distinct genera” (Darwin 1859). Sympatric speciation is hypothesized as “the evolution of a new species from a surviving ancestral species while both continue to inhabit the same geographic region”.
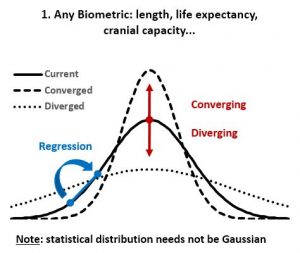
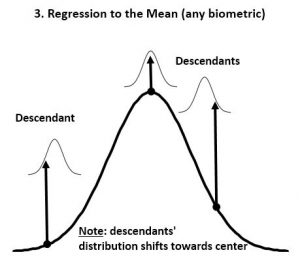
- ‘Regression to the mean’ is the biological law that overrules passive ‘Divergence of Character’. Any homogeneous population can be sorted statistically on various biologic metrics, usually resulting in a Gaussian (normal) distribution that is conserved over time in the absence of major environmental changes (as Mendel first showed; Fig 1&2). ‘Regression to the mean’ is thus the rule that causes the progeny of extreme individuals to be less extreme than their parents. Two outstanding tall parents will have statistically shorter children, and the progeny of the most and least intelligent/strong/aggressive/attractive/etc. will be more average than the parent. Many of the extremes have no descendants at all due to their limitations, and thus their “contribution” to the next generation is simply the average individual.
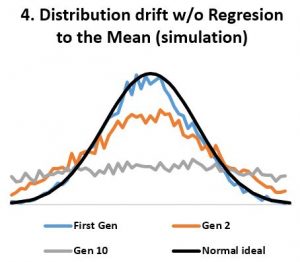
- In stable environments, population variability is extremely well conserved from generation to generation (Fig 3) as documented by the fossil and many other records. ‘Regression to the mean’ is thus a mathematical necessity without which a passive ‘divergence of character’ would be observed in very few generations (Fig 4). ‘Regression to the mean’ mechanism is incredibly accurate and allows for conservation of traits over thousands upon thousands of generations as observed. Scientists were rightfully surprised that ancient bacteria and many other fossils as well as mummified organisms including cats and monkeys are indistinguishable from their contemporary descendants. At a minimum, the number of organisms that show remarkable stability over long periods (living fossils) invalidate the ‘General Divergence’ theory. Does a limited, ‘Special Divergence’ hypothesis still make sense?
- Observed long term regression is highly unexpected and contrary to ‘divergence of character’ and ‘drift’ hypotheses. ‘Regression to the mean’ operates in the longest term observed, whenever environmental conditions are restored following significant changes that led to adaptive mutations. Most – if not all – organisms are endowed with a limited ‘plasticity’ trait that allows them to retain adaptive characteristics for generations. And yet, when the stimulus that caused the adaptation disappears, these organisms regress rather than maintaining those adaptive traits or accumulating even more diverging ones. Darwin’s finches, the peppered moth, antibiotic resistant bacteria and the domesticated plants & animals – all these and more have been observed to regress to the old mean when the adaptive stressor is removed, thus disproving even the limited, ‘Special Divergence’ hypothesis. These are not coincidences! The regression can happen over a few generations as in most epigenetic changes, many generations, and even the indefinite future if the adaptive stimulus is maintained (such as in domestication). Biologic variability can be compared to a loaded spring – the more it stretches, the harder the pull back (regression to the mean) and the more fragile is the extreme variant population. Domesticated plants and animals show that crossbreeds are resilient, while pure breeds are fragile showing that extinction of the extremes is the default outcome that promotes the ‘regression to the mean’ of the extended population.
- Adaptation neither demands not implies divergence in any way. What about the ‘adaptive radiation’ seen in Darwin’s finches, the cichlids of the African Great Lakes, and others? Is this not ‘divergence of character’? No. The driving force in all these and more is adaptation, not divergence even if “evolution” were true. Organisms just seek survival and, if their built-in yet limited plasticity matches the environmental challenges, these populations survive as variants. Otherwise, they simply go extinct like many others before. The new traits are not ‘divergent’ as shown by all known cases of reversals (as discussed) and none of further divergence when the adaptive stressor is removed. If ‘divergence of character’ were true, adaptive plasticity traits would be cumulative and sticky even after the adaptive stressor was removed, and the more extreme variants would be at least as resilient as the mean. Furthermore, experiments would show increasing variability over time in all research organisms and even more so in the short lived ones like bacteria. There would not be any distinct “species” and organisms would freely undergo metamorphosis (transmutation) into one another. Differential survival and randomness would eliminate all but the “best adapted” allele, therefore the Mendelian conservation of alleles would not be observed. Yet none of these are happening, thus falsifying the ‘divergence of character’ hypothesis.
- Adaptation is “fast and done”, “do or die” by necessity, unlike the supposed “slow and ongoing” ‘divergence of character’. If adaptation is not fast enough, the population simply goes extinct as many others did. The cichlids of Lake Victoria had less than 15,000 years to adapt and are as diverse if not more so than the cichlids in the other, much older African Great Lakes. But they do not need even that much time as the newer aquarium varieties obtained in a few generations show. Most likely, cichlids variants have come and gone throughout the history of all African Great Lakes in short cycles of adaptation. And that is why the cichlid biodiversity difference between a few years (Lake Victoria) and millions of years (other African Great Lakes) is unremarkable. The only remarkable fact is that cichlids have a predominantly Gondwanan distribution showing that in 180+ mil years, they did not adapt to ocean living despite their otherwise high adaptability. This clearly shows the limitations of adaptability and makes it an unlikely substitute to ‘divergence of character’. Darwin’s finches, peppered moths, bacteria, and many other also adapt fast or die as observed. And when the stimulus disappears, they revert just as quickly, and later readapt to whatever new stimulus they face or simply die out trying as confirmed. It is a very good thing ‘divergence of character’ is false, or else antibiotic resistant bacteria and other superbugs would have killed mankind by now as “evolution” falsely predicted.
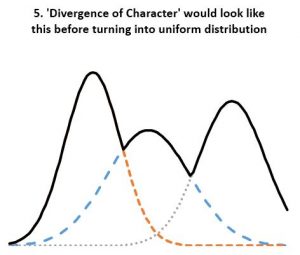
- Statistical evidence refutes ‘divergence of character’. According to the theory, “when organisms compete for scarce resources, natural selection should favor those individuals that are least like their competitors”. And since organisms always “compete for scarce resources”, the least average members of a homogenous population should always be favored by “natural selection”. If so, the well known normal distribution of any organism dimension (length, height, weight, etc.) should always be under pressure to change. We should see groups of “least like” the average form second, third, and so on normal distributions of their own, thus reshaping the original normal distribution into a composite distribution with several peaks and valleys as in Fig 5. And even that should not be adequate, as any concentration of similar individuals would be disadvantaged according to the ‘Divergence of character’ hypothesis, thus leading to uniform distributions as in Fig 4. However, neither Fig 5 nor uniform distributions are seen in homogeneous populations. Instead, we always see normal distributions. And since we see the normal distribution maintained over arbitrary number of generations and no hint of transitioning to a uniform distribution, the ‘Divergence of character’ hypothesis must be discarded. A trend not supported by several period observations must be discarded as noise artifact. This is the case for all examples considered including Darwin’s finches, the peppered moth, antibiotic resistant bacteria, cichlids, etc. All seem somewhat supportive of the divergence hypothesis over carefully chosen periods, yet the divergence is clearly illusory over longer periods.
- Are the bear of North America not like Fig 5? Yes, but they occupy different geographic regions. They are not homogenous. Indeed, we do encounter subfamilies of organisms, that have normally distributed metrics within the subgroup yet clearly distinct from those of other subgroups. However, where these subgroups overlap, the blend is always geographic and never biologic, meaning we see fewer of one kind and more of the other when moving from one’s territory to the others’ instead of blended characteristics as ‘divergence of character’ would predict. Humans are not different “species” although various subgroups are exclusively vegan/carnivorous, white/black, extra small/large. And domesticated organisms including canids are even more diverse than humans. Are the wild cichlids, finches, mice, and others qualitatively different than humans and canids? No. Then why the different “species”, many of which, ironically, are threatened by hybridization? The unwarranted inflation of “species” that do not even meet the loosest definition of reproductive isolation has the sole purpose of perpetuating the myth of ‘divergence of character’.
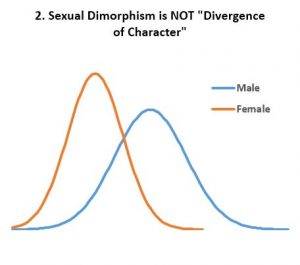
- Multimodal distributions in homogenous populations are not due to ‘divergence of character’. Indeed, bimodal distributions (Fig 2) and multimodal distributions are not uncommon in homogenous populations. However, these are due to the discreteness of physics in general and biology in particular, not due to ‘divergence of character’. Male and female populations are not diverging from one another and various alleles are in long term cyclical equilibrium as shown (spring model). ‘Drift’ is often invoked as a mechanism of ‘divergence of character’. This is wrong because ‘drift’ explains nothing as it is either aimless noise or due to adaptation and environmental change. Yet, as shown, adaptation is in no way ‘divergence of character’. In addition, the stable coexistence of several distinct variants within a homogenous population shows “gradualism”, “survival of the fittest”, and “natural selection” to be false because the alleles responsible are themselves distinct (no “gradualism”), they all “survive”, and neither is “selected” for or against.
- Darwin worried about regression to the mean for the wrong reasons. Namely, if blending inheritance (Darwin laid an egg) was true, then natural selection could not be true. Darwin puzzled over this a lot, but ended up with nothing satisfactory. Then Mendel showed that inheritance is discrete, not blended. Mendelian Inheritance Tables (see Punnett squares / Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium) show “probabilistic traits conservation” and thus disproving ‘divergence of character’ (at least as byproduct of reproduction) as well as dismissing “gradualism” (another one of Darwin’s unsupported claims).
- When entire populations split, do subgroups diverge from one another? This is not how ‘divergence of character’ is supposed to work. Descendants are supposed to diversify within the homogenous population. Furthermore, populations split by environmental conditions simply adapt to the new environment and for as long as those conditions allow. Adaptation is the driving force with no ‘divergence of character’ anywhere in sight. Island biology is the most diverse because islands are isolated and have many microenvironments. However, island variants are close descendants of their original colonists, showing that no divergence ever happened. Their risk of hybridization is high, disproving the “speciation” claim. They are also fragile examples of the extreme stretched biological spring model discussed, and will likely go extinct if at all stressed and when interacting with mainland.
Summary:
- ‘Regression to the mean’ is the biological law that overrules passive ‘Divergence of Character’
- In stable environments, population variability is extremely well conserved from generation to generation
- Observed long term regression is highly unexpected and contrary to ‘divergence of character’ and ‘drift’ hypotheses
- Adaptation neither demands not implies ‘divergence of character’ in any way
- Adaptation is “fast and done”, “do or die” by necessity, unlike the supposed “slow and ongoing” ‘divergence of character’
- Adaptation has limited powers and is thus not a substitute for ‘divergence of character’
- ‘Divergence of character’ hypothesis would lead to uniform rather than normal (Gaussian) distributions as observed in homogenous populations
- A trend not supported by several period observations must be discarded as noise artifact
- The unwarranted inflation of “species” that do not even meet the loosest definition of reproductive isolation has the sole purpose of perpetuating the myth of ‘divergence of character’
- Multimodal distributions in homogenous populations are not due to ‘divergence of character’
- Mendelian tables show “probabilistic traits conservation”, disproving ‘divergence of character’ (at least as byproduct of reproduction), as well as dismissing ‘gradualism’
- Island biology proves adaptation and the biologic spring model while disproving ‘divergence of character’
- What’s in, what’s out? IN: ‘regression to the mean’, ‘adaptation’, coexisting variants, long term stability, spring model, normal distributions. OUT: ‘divergence of character’, gradualism, drift, speciation, uniform distributions, “natural selection”, “survival of the fittest”, “evolution”
Pro-Con Notes
Con: Why can’t the ‘mean’ in the ‘regression to the mean’ be moving freely as in ‘divergence of character’?
Pro: It could if there were any evidence for it. But ‘living fossils’ among other evidence refutes a drift of the mean into new ‘character’. Also, not how ‘divergence of character’ is supposed to work according to Darwin: “when organisms compete for scarce resources, natural selection should favor those individuals that are least like their competitors”.
Links:
https://ucmp.berkeley.edu/bacteria/bacteriafr.html
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2019/10/191018112136.htm
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3285564/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3352989/
http://www.galton.org/essays/1880-1889/galton-1886-jaigi-regression-stature.pdf
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Character_displacement
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sympatric_speciation
https://www.bionity.com/en/encyclopedia/Character_displacement.html
https://biologydictionary.net/divergent-evolution/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cichlid
https://biology.stackexchange.com/questions/41982/regression-to-the-mean-and-evolution